“Unearthing Hidden Gems: 10 Intriguing Facts About the Champions League”
Giant Cell Tumor Homeopathic Treatment is the need today to treat and cure GCT naturally.
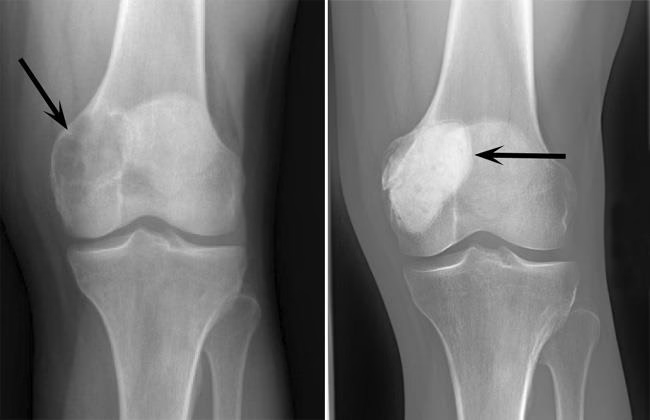
Giant Cell Tumor Homeopathic Treatment: A Natural Approach to Support Healing
Introduction to Giant Cell Tumors (GCT)
Giant Cell Tumorshttps://www.drkkpandey.com/giant-cell-tumor-precautions/ (GCTs) are uncommon, typically benign bone tumors known for their unpredictable behavior. Though non-cancerous, they can be locally aggressive, causing pain, bone damage, and limited mobility. Most often affecting adults aged 20–40, GCTs frequently develop near joints like the knees, wrists, or shoulders. Early diagnosis and a balanced treatment plan are key to managing symptoms and preserving quality of life.
Understanding the Causes of Giant Cell Tumor (GCT): What We Know
Giant cell tumors (GCTs) are intriguing yet poorly understood bone lesions. While they are classified as benign, their locally aggressive nature and tendency to recur make them a focus of medical research. The exact cause of GCTs remains unclear, but studies suggest a combination of genetic, cellular, and molecular factors may contribute to their development. Below, we break down the current understanding of GCT origins.
1. Genetic Mutations and Chromosomal Abnormalities
- H3F3A Gene Mutation: A key discovery in GCT research is the frequent mutation of the H3F3A gene, which encodes a histone protein involved in DNA organization. This mutation is found in nearly 90% of GCT cases and is believed to drive tumor growth by disrupting normal cellular processes.
- Chromosomal Instability: Abnormalities in chromosomes (e.g., telomeric associations) are common in GCT cells, though their direct role in tumor formation is still being studied.
2. Cellular Imbalance in Bone Remodeling
GCTs arise from the osteoclasts, cells responsible for breaking down bone tissue during remodeling. The tumors contain an overabundance of:
- Multinucleated Giant Cells: These large cells (which give the tumor its name) fuse with osteoclasts, creating an imbalance in bone breakdown and repair.
- Stromal Cells: Abnormal stromal (connective tissue) cells secrete signals like RANK Ligand (RANKL), which stimulate osteoclast activity, leading to excessive bone destruction.
3. Hormonal and Inflammatory Influences
- RANKL Signaling: Overexpression of RANKL (a protein involved in bone metabolism) in GCTs accelerates osteoclast formation, contributing to bone erosion.
- Inflammatory Cytokines: Pro-inflammatory molecules like interleukin-6 (IL-6) may create a microenvironment that supports tumor growth.
4. Age and Gender Factors
- Age: GCTs predominantly affect adults aged 20–40, suggesting hormonal or developmental factors during early adulthood may play a role.
- Gender: Some studies note a slight female predominance, though the reason is unknown.
5. Risk Factors and Associations
While no direct lifestyle or environmental cause has been identified, certain conditions are linked to GCT development:
- Paget’s Disease of Bone: A rare bone disorder associated with abnormal bone remodeling.
- Prior Radiation Exposure: Rare cases have been reported in bones previously exposed to radiation therapy.
Debunking Myths: What Does NOT Cause GCT
- Trauma: Injuries do not cause GCTs, though they may draw attention to an existing tumor.
- Diet or Lifestyle: No evidence links GCTs to nutrition, stress, or environmental toxins.
- Cancer: GCTs are benign, though their aggressive behavior can mimic malignancy.
The Big Picture
While research continues to unravel the complex origins of GCTs, the interplay of genetic mutations, cellular dysfunction, and bone remodeling imbalances appears central to their development. Unlike cancers, GCTs do not spread to distant organs but can cause significant local damage if untreated.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
GCTs often present with:
– Persistent pain near a joint, worsening at night.
– Swelling or a palpable lump.
– Reduced range of motion.
– Rarely, fractures due to bone weakening.
Diagnosis involves imaging (X-rays, MRI) and a biopsy to confirm the tumor’s nature. While surgery remains the primary treatment, recurrence rates are notable, prompting interest in complementary therapies like homeopathy.
Conventional Treatments
Standard approaches include:
– **Curettage**: Surgical removal of the tumor.
– **Bone Grafts/Implants**: To restore bone structure.
– Radiation Therapy: For inoperable cases.
– **Medications**: Bisphosphonates to inhibit bone loss.
While effective, these methods may have side effects, leading patients to explore holistic options for symptom relief and recovery support.
Giant Cell Tumor Homeopathic Treatment: The Homeopathic Approach
Homeopathy, a 200-year-old natural medicine system, focuses on stimulating the body’s self-healing mechanisms. It uses highly diluted substances to address physical and emotional imbalances. For GCTs, homeopathy aims to:
– Alleviate pain and inflammation.
– Strengthen bone health.
– Reduce recurrence risk.
– Enhance overall well-being.
*Important Note*: Homeopathy should complement, not replace, conventional treatments. Always consult healthcare providers before integrating new therapies.
Common Homeopathic Remedies for GCT Support
1. **Calcarea Fluorica**: Strengthens bones and connective tissues; useful for hard, bony swellings.
2. **Hekla Lava**: Derived from volcanic ash, it’s traditionally used for bone spurs and tumors.
3. **Silicea**: Promotes expulsion of foreign bodies (e.g., bone fragments) and supports healing.
4. **Symphytum**: “Bone knit” remedy for fractures and post-surgery recovery.
5. **Ruta Graveolens**: Eases joint stiffness and bone pain, especially after injury.
*Remedies are tailored to individual symptoms by a licensed homeopath.*
**Integrating Homeopathy with Conventional Care**
A holistic strategy might include:
– Using homeopathy to manage post-surgery pain or fatigue.
– Combining remedies with physiotherapy to improve mobility.
– Addressing stress or anxiety linked to chronic illness through personalized homeopathic care.
FAQs
Q: Can homeopathy cure giant cell tumors?*
A: Homeopathy doesn’t “cure” GCTs but may aid symptom management and recovery alongside conventional treatments.
*Q: Is homeopathy safe for long-term use?*
A: Generally safe, but work with a qualified practitioner to ensure compatibility with your health plan.
*Q: How soon can results be expected?*
A: Responses vary; some notice changes in weeks, others over months. Consistency and patience are vital.
Conclusion
Giant Cell Tumors require a multifaceted treatment approach. Homeopathy offers a gentle, natural way to support healing, reduce discomfort, and enhance resilience. By blending modern medicine with holistic care, patients can navigate their health journey with greater confidence.
*Always consult your medical team before trying new therapies. Your health deserves a collaborative, informed approach.*
—
**SEO Keywords**: Giant cell tumor homeopathic treatment, natural remedies for GCT, homeopathy for bone tumors, benign bone tumor support, holistic GCT management.

