Genetic disorders, mysterious yet significant, exert a profound impact on individual health. From anomalies in single genes to intricate chromosomal variations, these conditions present unique challenges. This article delves into the depths of genetic disorders, exploring types, causes, societal impact, and the relentless efforts in research and advocacy.
Outline
Table of Contents
- 1 Outline
- 2 Genetic Disorders: Understand the Complexities of Human Health through Genetic Codes.
- 2.1 I. Introduction
- 2.2 II. Varieties of Genetic Disorders
- 2.3 III. What are The Causes of Genetic Disorders and Risk Factors?
- 2.4 IV. Common Genetic Disorders
- 2.5 V. Genetic Disorder Testing and Diagnosis
- 2.6 VI. Treatment and Management
- 2.7 VII. Future Prospects in Genetic Disorders Research
- 2.8 VIII. Impact on Families and Society
- 2.9 IX. Dispelling Myths and Stigmas
- 2.10 X. Strategies for Coping
- 2.11 XI. Research and Advocacy Initiatives
- 2.12 XII. Triumph Stories
- 2.13 XIII. Government and Policies
- 2.14 XIV. Challenges in Management of Genetic Disorders-
- 2.15 XV. Conclusion
- 3 FAQs
I. Introduction
A. Defining Genetic Disorders
B. Importance of Understanding Genetic Disorders
II. Varieties of Genetic Disorders
A. Single-Gene Conditions
B. Chromosomal Aberrations
C. Multifaceted Disorders
D. Disorders Linked to Mitochondria
III. Causes and Risk Factors
A. Origins of Genetic Mutations
B. Transmission of Inherited Genetic Material
C. Influence of Environmental Factors
D. Advances in Genetic Research
IV. Common Genetic Disorders
A. Insight into Down Syndrome
B. Understanding Cystic Fibrosis
C. Navigating Hemophilia
D. The Challenges of Huntington’s Disease
V. Genetic Testing and Diagnosis
A. Significance of Genetic Testing
B. Diverse Screening Methods
C. Necessity for Counseling in Genetic Disorders
VI. Treatment and Management
A. Medicinal Approaches and Therapies
B. Surgical Interventions
C. Embracing Supportive Care and Lifestyle Adjustments
VII. Future Prospects in Genetic Disorder Research
A. CRISPR Technology: A Revolutionary Approach
B. Advancements in Gene Therapy
C. Navigating Ethical Considerations
VIII. Impact on Families and Society
A. Emotional Journeys of Affected Families
B. Building Robust Support Systems
C. Fostering Societal Awareness
IX. Dispelling Myths and Stigmas
A. Educating Against Misconceptions
B. Advocating for Inclusivity and Understanding
X. Strategies for Coping
A. Forging Support Networks
B. Empowering Through Education
XI. Research and Advocacy Initiatives
A. Organizations Spearheading Genetic Disorder Initiatives
B. Advocacy for Research Funding
C. Driving Public Awareness
XII. Triumph Stories
A. Narratives of Overcoming Genetic Challenges
B. Positive Impact of Supportive Communities
XIII. Government and Policies
A. Legislative Measures in Genetic Disorder Management
B. Ensuring Access to Healthcare
XIV. Challenges in Management
A. Tackling Treatment Accessibility Issues
B. Alleviating Financial Strain on Families
XV. Conclusion
A. Summarizing Key Insights
B. Encouraging Ongoing Research and Support
Genetic Disorders: Understand the Complexities of Human Health through Genetic Codes.
I. Introduction
Genes are the carrier of the all characters which are found in mother and father. Genes are made up of DNA, which are made up of proteins. If any changes occur in the structure of the protein due to mutation. Then the protein doesn’t perform their original work and do unnecessary different works, which is called genetic disorder.
Defining Genetic Disorders
Genetic disorders result from abnormalities in an individual’s DNA, encompassing mutations in a single gene, chromosomal irregularities, or a fusion of genetic and environmental factors.
Importance of Understanding Genetic Disorders
Comprehending genetic disorders is pivotal for early diagnosis, proactive management, and ongoing medical progress. Unraveling the complexities can usher in innovative therapeutic interventions.
II. Varieties of Genetic Disorders
1. Single-Gene Conditions
Derived from mutations in a single gene, these Mendelian disorders include examples like cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anemia.
2. Chromosomal Aberrations
Structural or numerical irregularities in chromosomes lead to chromosomal disorders, exemplified by Down syndrome.
3. Multifaceted Disorders
Arising from a blend of genetic and environmental factors, conditions like diabetes and heart disease fall into this category.
4. Disorders Linked to Mitochondria
Mitochondrial disorders affecting cellular energy production underline challenges like muscle weakness and neurological problems.
III. What are The Causes of Genetic Disorders and Risk Factors?
Origins of Genetic Mutations
Genetic mutations can spontaneously occur or be inherited, necessitating an understanding of mutation types for gauging the risk of genetic disorders and it is valuable to find the origin of the disease.
Transmission of Inherited Genetic Material
Certain disorders follow familial patterns, emphasizing the importance of familial history in diagnosis and risk assessment.
Influence of Environmental Factors
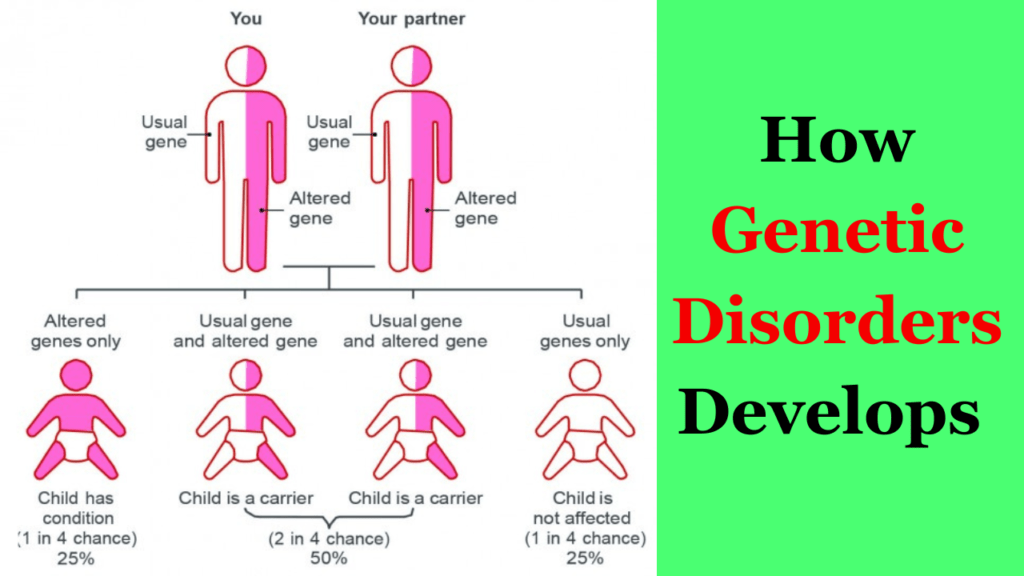
There is no evidence are found to affect genetic disorders by any environmental situation, which is a good thing for the person but we have to aware this factor.
Advances in Genetic Disorders Research
Ongoing breakthroughs in genetic research, which includes precision medicine and CRISPR technology, It can be promise targeted approaches to managing genetic disorders.
IV. Common Genetic Disorders
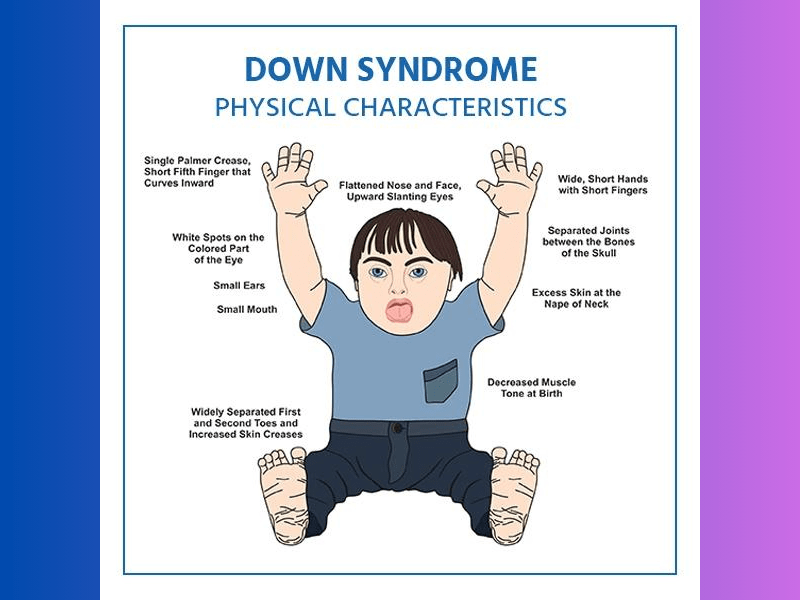
1. Insight into Down Syndrome
Down syndrome, which is a chromosomal disorder. It is characterized by intellectual disabilities. Unique physical features such as flat nose, short hands, small ears and also small mouth and many more symptoms are found. It is beneficial for the patient early intervention and support services.
2. Understanding Cystic Fibrosis
A hereditary disorder impacting respiratory and digestive systems,which is characterized by a constant cough which causes large amount of sputum, repeated lung infections and many more symptoms are find. Cystic fibrosis sees improved treatment options, including gene therapies.
3. Navigating Hemophilia
Hemophilia, which is a blood clotting disorder. In this disease, blood cannot be coagulated when any bleeding occurs. Underscores the significance of genetic testing for carrier detection and family planning.
4. The Challenges of Huntington’s Disease
A progressive neurodegenerative disorder that is Huntington’s disease which emphasizes the need for comprehensive care in genetic disorder.
V. Genetic Disorder Testing and Diagnosis
Significance of Genetic Disorder Testing
Genetic testing plays a pivotal role in identifying at-risk individuals, which is enabling timely intervention, and contributing to accurate diagnoses.
Diverse Screening Methods
Screening methods, which works from newborn screenings to prenatal testing, and facilitate early detection, also allowing for prompt medical interventions.
Necessity for Counseling in Genetic Disorder
Genetic counseling provides essential information regarding genetic disorders which can aid individuals and families in making informed decisions about their health and family planning.
VI. Treatment and Management
Medicinal Approaches and Therapies
Advancements in medical treatments, including targeted medications and therapeutic interventions, are enhancing outcomes for genetic disorder sufferers. In this era we have the most effective mode of treatment that is homeopathy, which is the most important to treat any genetic disorder as compare to any mode of treatments.
Surgical Interventions in Genetic Disorder
In some cases, surgical interventions become necessary to address the physical manifestations of genetic disorder but in spite of that we recommend homeopathy to treat without surgery.
Embracing Supportive Care and Lifestyle Adjustments
Supportive care, including physical therapy and lifestyle modifications, which can play a vital role in managing symptoms and improving overall well-being.
Homeopathic medication
This is the best way to treat genetic diseasesin a easy manner without surgery. Homeopathy can remove the symptoms of the disease and cur permanently. If we treat on the basis of constitution of the patient, it can helpful for the patient to treat any genetic disorder easily. For more information about treatment visit on the link.
VII. Future Prospects in Genetic Disorders Research
CRISPR Technology: A Revolutionary Approach
CRISPR technology holds immense potential for editing genetic material, opening up new possibilities for treating and preventing genetic disorders.
Advancements in Gene Therapy
Ongoing developments in gene therapy offers hope for targeted and personalized treatment options for individuals with genetic disorder which will be beneficial for all the genetic disorder patients.
Navigating Ethical Considerations
As technology advances, addressing ethical concerns surrounding genetic interventions becomes paramount to ensuring responsible and equitable use.
VIII. Impact on Families and Society
Emotional Journeys of Affected Families
The emotional impact of genetic disorders on individuals and families underscores the need for robust mental health support services. During genetic disorder not only the patient, but also their family members are also affected.
Building Robust Support Systems
Building strong support networks are essential families in navigating the challenges associated with genetic disorders.
Fostering Societal Awareness
Increasing awareness and understanding of genetic disorder in society can contribute to reducing stigma and fostering inclusivity.
IX. Dispelling Myths and Stigmas
Educating Against Misconceptions
Educating the public and dispelling myths surrounding genetic disorder is crucial for creating a more compassionate and informed society.
Advocating for Inclusivity and Understanding
Promoting inclusivity involves recognizing the abilities and potential of individuals with genetic disorders, fostering a more inclusive and supportive community
X. Strategies for Coping
Forging Support Networks
Connecting with other families facing similar challenges provides emotional support and shared experiences.
Empowering Through Education
Empowering individuals with genetic disorder through education and advocacy enhances their ability to navigate the complexities of their condition.
XI. Research and Advocacy Initiatives
Organizations Spearheading Genetic Disorder Initiatives
Highlighting organizations dedicated to supporting individuals with genetic disorders and advancing research initiatives.
Advocacy for Research Funding
Advocating for increased funding for genetic disorder research ensures continued progress in understanding and managing these conditions.
Driving Public Awareness
Engaging in awareness campaigns helps disseminate accurate information and reduce the stigma associated with genetic disorders.
XII. Triumph Stories
Narratives of Overcoming Genetic Challenges
Sharing inspiring stories of individuals who have overcome the challenges posed by genetic disorders.
Positive Impact of Supportive Communities
Emphasizing the positive influence of supportive communities in the journey of individuals and families affected by genetic disorders.
XIII. Government and Policies
Legislative Measures in Genetic Disorder Management
Examining the role of government in enacting policies that support individuals with genetic disorders, including access to healthcare and social services.
Ensuring Access to Healthcare
Ensuring equitable access to healthcare services is crucial for individuals with genetic disorder to receive timely and effective treatments.
XIV. Challenges in Management of Genetic Disorders-
Tackling Treatment Accessibility Issues
Addressing challenges related to the accessibility of specialized treatments and therapies for individuals with genetic disorders.
Alleviating Financial Strain on Families
Recognizing and mitigating the financial burden on families coping with the long-term management of genetic disorders.
XV. Conclusion
Summarizing Key Insights Of Genetic Disorders
Genetic disorders are diverse and complex, impacting individuals and families in various ways. Understanding these conditions is essential for early diagnosis, effective management, and ongoing research.
Encouraging Ongoing Research and Support
Supporting research initiatives and advocating for policies that enhance the quality of life for individuals with genetic disorder is a collective responsibility.
FAQs
- Can genetic disorder be prevented through lifestyle changes?
Genetic disorders, being primarily rooted in DNA, may not be preventable through lifestyle changes. However, a healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall well-being. - How can individuals find support for coping with a genetic disorder diagnosis?
Support groups, including counseling services, and advocacy organizations are valuable resources for individuals and families facing genetic disorders. - What role does genetic counseling play in family planning?
Genetic counseling provides crucial information about the risk of passing on genetic disorders, aiding individuals and couples in making informed family planning decisions. - Are there ongoing clinical trials for new treatments of genetic disorders?
Yes, many clinical trials are underway, exploring innovative treatments and therapies for various genetic disorders. - How can society contribute to reducing the stigma surrounding genetic disorders?
Society can contribute by promoting awareness, understanding, and inclusivity, thereby fostering a more supportive environment for individuals with genetic disorders.



