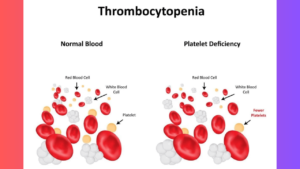
Thrombocytopenia is a medical condition characterized by a low platelet count in the blood. Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, are crucial for blood clotting and preventing excessive bleeding. When the platelet count drops below normal levels, it can lead to increased risk of bleeding and bruising. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for it.
What Causes Thrombocytopenia?
Table of Contents
It can be caused by various factors, including:
1. Medical Conditions:
Underlying medical conditions such as leukemia, aplastic anemia, and liver disease can lead to thrombocytopenia. These conditions may affect the production of platelets or cause increased destruction of platelets in the bloodstream.
2. Medications:
Certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs, antibiotics, and anti-seizure medications, can lower platelet counts as a side effect. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional about potential side effects of medications.
3. Autoimmune Disorders:
Autoimmune disorders like immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) can result in the immune system mistakenly attacking and destroying platelets, leading to thrombocytopenia.
4. Infections:
Viral or bacterial infections such as HIV, hepatitis C, or H. pylori can sometimes cause thrombocytopenia by affecting the bone marrow’s ability to produce platelets.
Symptoms of Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia may present with the following symptoms:
1- Excessive bruising
2- Petechiae (small red or purple spots on the skin)
3- Bleeding gums
4- Nosebleeds
5- Heavy menstrual periods
6- Blood in urine or stool
7- Prolonged bleeding from cuts or injuries
It’s essential to seek medical attention if experiencing any of these symptoms, as untreated thrombocytopenia can lead to severe complications.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing thrombocytopenia typically involves a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and blood tests to measure platelet counts. Additional tests may be necessary to determine the underlying cause of thrombocytopenia.
Treatment Options:
The treatment for thrombocytopenia depends on its underlying cause and severity. Treatment options may include:
1. Medications:
– Corticosteroids: These medications can help suppress the immune system and prevent it from attacking platelets in cases of autoimmune thrombocytopenia.
– Immune Globulin Therapy: Intravenous infusions of immune globulin can help increase platelet counts in certain autoimmune disorders.
– Thrombopoietin Receptor Agonists: These drugs stimulate the production of platelets in the bone marrow and can be used to treat chronic thrombocytopenia.
2. Platelet Transfusions:
In severe cases of thrombocytopenia with active bleeding or very low platelet counts, platelet transfusions may be necessary to prevent or treat bleeding complications.
3. Splenectomy:
In cases where the spleen is removing platelets from circulation at an accelerated rate, surgical removal of the spleen (splenectomy) may be recommended to improve platelet counts.
4. Treatment of Underlying Conditions:
Addressing underlying medical conditions or infections that contribute to thrombocytopenia is essential for effective management.
Thrombocytopenia and homeopathic treatment
Thrombocytopenia, characterized by a low platelet count in the blood, can be a concerning condition that requires medical attention and management. Some homeopathic remedies may be explored under the guidance of a qualified homeopath or healthcare provider. Here are some potential homeopathic treatments that may be considered:
1. Arnica montana:
– Arnica montana is a commonly used homeopathic remedy that is believed to help reduce bruising and promote healing. It may be considered for individuals with thrombocytopenia who experience excessive bruising or bleeding.
2. Phosphorus:
– Phosphorus is another homeopathic remedy that is sometimes recommended for individuals with bleeding disorders. It is thought to help improve blood clotting and reduce bleeding tendencies.
3. Lachesis:
– Lachesis is a homeopathic remedy derived from the venom of the bushmaster snake. It is often used in cases of hemorrhage or excessive bleeding and may be considered for individuals with thrombocytopenia who experience bleeding symptoms.
4. Apis mellifica:
– Apis mellifica, derived from the honeybee, is sometimes used in homeopathy for conditions involving inflammation and swelling. It may be considered for individuals with thrombocytopenia who experience symptoms such as swelling or inflammation of the skin or mucous membranes.
5. Natrum muriaticum:
– Natrum muriaticum, or common salt, is used in homeopathy for various conditions, including those involving fluid balance and circulation. It may be considered for individuals with thrombocytopenia who experience symptoms such as excessive thirst or dryness of mucous membranes.
It’s essential to consult with a qualified homeopath or healthcare provider before using any homeopathic remedies, especially for a serious medical condition like thrombocytopenia. Homeopathic treatment should always be integrated into a comprehensive care plan that includes conventional medical management and regular monitoring by healthcare professionals. Additionally, individuals with thrombocytopenia should follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations for treatment and monitoring to ensure optimal health outcomes.
Thrombocytopenia icd 10
Thrombocytopenia icd 10 is a classification under the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10) coding system. The specific code for thrombocytopenia in ICD-10 is D69.6. This code is used by healthcare professionals to document and classify cases of thrombocytopenia for medical billing, statistical analysis, and research purposes. It can have various underlying causes and manifestations, but Thrombocytopenia ICD-10 code remains consistent for coding and documentation purposes across healthcare settings.
Conclusion
Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by low platelet counts in the blood, which can lead to increased bleeding and bruising. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for thrombocytopenia is crucial for proper management and prevention of complications. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of thrombocytopenia, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.





[…] 1. Bleeding: […]