The treatment for annular fissures can be a valuable resource for individuals seeking information on managing this condition.
What are Annular Fissures ?
Table of Contents
- 1 What are Annular Fissures ?
- 2 Causes
- 3 Symptoms of Annular fissures
- 4 Diagnostic Procedures
- 5 Treatment for Annular Fissures:
- 6 1. Conservative Treatment Options
- 7 Benefits and limitations of conservative treatments in managing annular fissures
- 8 Benefits of Conservative Treatments:
- 9 Limitations of Conservative Treatments:
- 10 2. Interventional Treatments
- 11 3. Surgical Interventions
- 12 4. Emerging Therapies and Research
- 13 Lifestyle Modifications and Preventive Measures
- 14 Conclusion
- 15 References
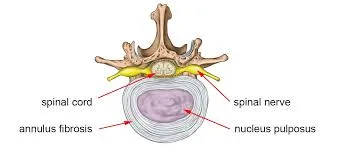
Annular fissures are small tears or cracks in the outer layer of the intervertebral discs in the spine, known as the annulus fibrosus. They can result from various factors such as aging, trauma, or repetitive stress.
Significance in spinal health
Their significance in spinal health lies in their potential to cause symptoms such as localized or radiating pain, reduced mobility, and nerve compression. Annular fissures can lead to conditions like disc herniation, where the inner gel-like material of the disc protrudes through the fissure, causing pressure on spinal nerves and resulting in pain and other neurological symptoms.
Understanding annular fissures is essential as they can contribute to chronic pain and functional impairment if left untreated, emphasizing the importance of proper diagnosis and management to maintain spinal health and overall well-being.
Brief overview of the impact of annular fissures on daily life and mobility
Annular fissures can significantly impact daily life and mobility. They often cause persistent pain, which can vary in intensity and location depending on the severity and location of the fissure. This pain can interfere with routine activities such as sitting, standing, walking, or lifting objects. Additionally, annular fissures may limit flexibility and range of motion in the spine, making it challenging to perform everyday tasks comfortably. In severe cases, nerve compression resulting from annular fissures can lead to radiating pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the limbs, further affecting mobility and overall quality of life. Addressing annular fissures through appropriate treatment and management strategies is essential to minimize their impact on daily activities and maintain optimal mobility and function.
Causes
These fissures can develop due to various factors, including:
1. Age-related degeneration:
As we get older, the discs between our vertebrae lose water and flexibility, which makes them easier to tear and damage. Inadequate quantity of water intake.
2. Trauma:
Sudden injuries or trauma, such as a fall or accident, can cause annular fissures.
3. Repetitive stress:
Continuous or repetitive movements or activities that strain the spine, such as heavy lifting or poor posture, can contribute to the development of fissures over time.
Symptoms of Annular fissures
1. Localized or radiating pain:
Patients may experience pain in the affected area of the spine or pain that radiates to other parts of the body, such as the buttocks, legs, or arms, depending on the location of the fissure and whether it affects nearby nerves.
2. Stiffness and reduced mobility:
Annular fissures can cause stiffness and limited range of motion in the spine, making it difficult to perform certain movements comfortably.
3. Nerve compression symptoms:
In cases where the fissure leads to disc herniation or nerve compression, patients may experience additional symptoms such as numbness, tingling, weakness, or muscle spasms in the affected area.
It’s important to note that not all annular fissures cause symptoms, and the severity of symptoms can vary from person to person. However, if left untreated, annular fissures can worsen over time and lead to chronic pain and functional limitations, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis and appropriate management.
Clarification of how annular fissures relate to conditions like disc herniation and degenerative disc disease-
Annular fissures are closely related to conditions like disc herniation and degenerative disc disease:
1. Disc Herniation:
Annular fissures can predispose the intervertebral discs to herniation. When a fissure weakens the outer layer (annulus fibrosus) of a disc, the inner gel-like material (nucleus pulposus) can protrude through the tear, causing a disc herniation. This protrusion can compress nearby spinal nerves, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness in the affected area or radiating down the arms or legs, depending on the location of the herniated disc.
2. Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD):
Annular fissures are often a hallmark of degenerative disc disease, a condition characterized by the gradual breakdown of the intervertebral discs over time. As the discs degenerate, they become more susceptible to fissures and other structural changes. Annular fissures can accelerate the degenerative process by weakening the integrity of the discs, leading to decreased disc height, loss of disc hydration, and altered biomechanics in the spine. This degeneration can contribute to symptoms such as chronic back pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
In summary, annular fissures play a significant role in the pathogenesis of disc herniation and are a common feature of degenerative disc disease. Understanding these relationships is crucial for diagnosing and managing spinal conditions effectively.
Diagnostic Procedures
– Overview of diagnostic methods used to identify annular fissures, such as MRI and CT scans.
– Importance of accurate diagnosis in developing an effective treatment plan.
Treatment for Annular Fissures:
1. Conservative Treatment Options
Conservative treatment options for annular fissures focus on non-surgical approaches to alleviate symptoms, reduce inflammation, and promote healing of the damaged intervertebral discs. These methods are aimed at managing pain and improving function without the need for invasive procedures. Here are some conservative treatment options for annular fissures:
1. Rest:
Taking a break from activities that exacerbate symptoms can help reduce strain on the affected area and promote healing. Resting in a comfortable position, such as lying down with the knees bent or using supportive pillows, can relieve pressure on the spine and alleviate pain.
2. Physical Therapy:
Physical therapy plays a key role in the conservative management of annular fissures. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, improve flexibility, and correct posture. Additionally, modalities such as heat therapy, cold therapy, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation may be used to reduce pain and inflammation.
3. Medication:
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation associated with annular fissures but it has some side effects. On the other hand hoeopathic medicine has the power to reduce pain and heal the annular fissure also. Muscle relaxants may also be prescribed to ease muscle spasms in the affected area. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to provide targeted pain relief and reduce inflammation.
4. Activity Modification:
Modifying daily activities to avoid movements that worsen symptoms can help prevent further damage to the intervertebral discs. This may include avoiding heavy lifting, bending at the waist, or prolonged sitting or standing in one position. Using proper lifting techniques and ergonomic equipment can also help reduce strain on the spine.
5. Lifestyle Changes:
Making lifestyle modifications can support the healing process and improve overall spinal health. This may involve maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the spine, quitting smoking to promote tissue healing and reduce inflammation, and incorporating regular exercise to strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine and improve flexibility.
6. Pain Management Techniques:
In addition to medication, other pain management techniques such as acupuncture, massage therapy, and chiropractic care may provide relief from symptoms associated with annular fissures. These alternative therapies can help reduce pain, improve mobility, and enhance overall well-being.
Overall, conservative treatment options for annular fissures offer a comprehensive approach to managing symptoms and promoting spinal health. By combining rest, physical therapy, medication, activity modification, lifestyle changes, and pain management techniques, individuals with annular fissures can experience relief from pain and improve their quality of life without resorting to surgery.
Benefits and limitations of conservative treatments in managing annular fissures
Conservative treatments for managing annular fissures offer several benefits, but they also have limitations. Understanding these pros and cons can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment plan. Here’s an overview:
Benefits of Conservative Treatments:
1. Avoids Surgery:
One of the primary benefits of conservative treatments is that they allow individuals to avoid surgical intervention. Surgery carries inherent risks and may require a lengthy recovery period, so opting for non-invasive approaches can be preferable for many patients.
2. Promotes Natural Healing:
Conservative treatments focus on supporting the body’s natural healing processes. By addressing underlying issues such as inflammation, muscle imbalances, and poor posture, these treatments facilitate the healing of annular fissures without the need for invasive procedures.
3. Reduces Pain:
Many conservative treatments are effective at reducing pain associated with annular fissures. Techniques such as physical therapy, medication, and pain management modalities can provide significant relief, allowing individuals to improve their quality of life and resume normal activities.
4. Improves Functionality:
Through targeted exercises and lifestyle modifications, conservative treatments can improve spinal stability, flexibility, and overall functionality. This enables individuals to perform daily tasks with greater ease and reduces the risk of future injury.
5. Cost-Effective:
In general, conservative treatments are more cost-effective than surgical interventions. They typically involve fewer medical expenses, such as hospitalization and post-operative care, making them a more affordable option for many patients.
Limitations of Conservative Treatments:
1. May Take Time:
Unlike surgery, which can provide immediate relief in some cases, conservative treatments for annular fissures may take time to yield noticeable results. Patients may need to commit to a comprehensive treatment plan and be patient as they wait for symptoms to improve.
2. Not Always Effective:
While conservative treatments can be highly effective for many individuals, they may not provide sufficient relief for everyone. Some patients may require more aggressive interventions, such as surgery, if their symptoms are severe or do not respond to conservative measures.
3. Requires Compliance:
Successfully managing annular fissures with conservative treatments often requires strict adherence to treatment protocols. This may involve attending physical therapy sessions, taking medications as prescribed, and making lifestyle modifications, which can be challenging for some patients.
4. Potential Side Effects:
Certain conservative treatments, such as medications, may carry the risk of side effects. For example, NSAIDs can cause gastrointestinal issues, and corticosteroid injections may lead to temporary pain at the injection site. Patients should weigh the benefits against the potential risks when considering these options.
5. Limited in Severe Cases:
In cases where annular fissures cause severe symptoms or neurological deficits, conservative treatments alone may not be sufficient. Surgical intervention may be necessary to address the underlying structural issues and prevent further complications.
In conclusion, while conservative treatments offer several benefits in managing annular fissures, they also have limitations. Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a tailored treatment plan that addresses their individual needs and preferences while considering the benefits and risks of each approach.
2. Interventional Treatments
Interventional treatments for annular fissures involve more invasive procedures aimed at directly targeting the underlying cause of the condition. While conservative treatments focus on non-surgical approaches, interventional treatments may be considered when conservative measures fail to provide sufficient relief or when symptoms are severe. Here are some common interventional treatments for annular fissures:
1. Epidural Steroid Injections:
Epidural steroid injections involve the administration of corticosteroids directly into the epidural space surrounding the spinal nerves. These injections help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain associated with annular fissures. They can provide targeted relief and may be recommended for patients who experience significant pain despite conservative treatments.
2. Facet Joint Injections:
Facet joint injections target the small joints located between adjacent vertebrae in the spine. These injections typically contain a combination of local anesthetic and corticosteroid medication. Facet joint injections can help reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and improve mobility in patients with annular fissures affecting the facet joints.
3. Radiofrequency Ablation:
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a procedure that’s minimally invasive, using heat produced by radiofrequency energy to interrupt nerve signals that cause pain transmission. RFA is often used to treat chronic back pain caused by annular fissures or facet joint arthritis. It can provide long-lasting pain relief by temporarily disabling the nerves that transmit pain signals to the brain.
4. Percutaneous Discectomy:
Percutaneous discectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to treat herniated discs and annular fissures. During the procedure, a special device is inserted into the disc space through a small incision in the skin. The device is used to remove or shrink the damaged portion of the disc, relieving pressure on the spinal nerves and reducing pain.
5. Spinal Cord Stimulation:
Spinal cord stimulation (SCS) involves the implantation of a small device that delivers electrical impulses to the spinal cord. These impulses interfere with the transmission of pain signals to the brain, providing relief from chronic pain conditions such as annular fissures. SCS may be recommended for patients who have not responded to other interventional or conservative treatments.
6. Laser Disc Decompression:
Laser disc decompression is a minimally invasive procedure that uses laser energy to shrink and seal off the damaged portion of the intervertebral disc. This helps reduce pressure on the spinal nerves and alleviate pain associated with annular fissures. Laser disc decompression is typically performed on an outpatient basis and has a shorter recovery time compared to traditional surgery.
Interventional treatments for annular fissures offer targeted relief from pain and can help improve quality of life for patients who have not responded to conservative measures. Nevertheless, these procedures come with risks and may not be appropriate for all individuals. Patients should discuss their options with a qualified healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate course of treatment based on their individual needs and preferences.
3. Surgical Interventions
Surgical Options for Severe or Refractory Cases of Annular Fissures:
In severe or refractory cases of annular fissures, surgical intervention may be considered to address persistent symptoms and restore spinal function. Two common surgical options for annular fissures include:
- Discectomy: A discectomy is a surgical procedure aimed at removing a portion of the damaged intervertebral disc that is causing compression or irritation of nearby nerves. During the procedure, the surgeon makes a small incision in the back or neck and carefully removes the herniated or protruding disc material. This relieves pressure on the spinal nerves and can alleviate symptoms such as pain, numbness, and weakness.
- Spinal Fusion: Spinal fusion is a surgical procedure that involves joining two or more vertebrae together to stabilize the spine and prevent movement between them. This may be recommended for patients with severe instability or degeneration of the spine caused by annular fissures. During the procedure, the surgeon uses bone grafts, metal implants, or synthetic materials to fuse the affected vertebrae, promoting healing and stability.
Risks and Benefits of Surgical Intervention:
Risks:
- Infection: Like any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection at the surgical site.
- Nerve Damage: Surgery near the spinal nerves carries the risk of nerve damage, which can lead to sensory or motor deficits.
- Blood Loss: Surgery may involve blood loss, requiring transfusions in some cases.
- Failed Surgery: There is a possibility that the surgical outcome may not meet expectations, resulting in persistent symptoms or the need for additional procedures.
Benefits:
- Pain Relief: Surgery can provide significant relief from pain and other symptoms associated with annular fissures.
- Improved Functionality: Surgical intervention can restore spinal stability and function, allowing patients to resume normal activities.
- Prevention of Further Damage: Surgery may prevent further degeneration of the spine and reduce the risk of complications associated with untreated annular fissures.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: By addressing the underlying cause of symptoms, surgery can improve overall quality of life for patients with severe or refractory cases of annular fissures.
Importance of Patient Selection and Shared Decision-Making:
Patient selection is crucial when considering surgical intervention for annular fissures. Healthcare providers must carefully assess each patient’s medical history, symptoms, imaging studies, and overall health status to determine the most appropriate treatment approach. Additionally, shared decision-making between patients and healthcare providers is essential to ensure that treatment goals, expectations, and preferences are aligned.
Patients should be fully informed about the risks, benefits, and alternatives to surgery, allowing them to make informed decisions about their care. Shared decision-making empowers patients to participate actively in their treatment process, leading to better outcomes and improved patient satisfaction.
4. Emerging Therapies and Research
Promising Advancements in the Treatment of Annular Fissures:
Recent advancements in medical research have led to the exploration of innovative treatment approaches for annular fissures. Two promising advancements include:
1. Stem Cell Therapy:
Stem cell therapy holds significant potential for the treatment of annular fissures. Stem cells can differentiate into different types of cells, including those present in intervertebral discs. Injecting stem cells into the damaged disc tissue may promote regeneration and repair, leading to improved disc function and reduced symptoms. Early studies have shown promising results, although further research is needed to fully understand the safety and efficacy of this treatment approach.
2. Biologic Agents:
Biologic agents, such as growth factors, cytokines, and other proteins, have emerged as potential therapeutic options for annular fissures. These agents have the ability to modulate inflammation, promote tissue regeneration, and enhance healing processes within the intervertebral disc. By targeting specific pathways involved in disc degeneration and repair, biologic agents may offer a targeted and personalized approach to treating annular fissures.
Ongoing Clinical Trials and Potential Implications:
Several ongoing clinical trials are investigating the safety and efficacy of novel treatment approaches for annular fissures. These trials aim to evaluate the potential benefits of stem cell therapy, biologic agents, and other innovative interventions in larger patient populations. The results of these trials may have significant implications for the future of annular fissure treatment.
For example, if stem cell therapy demonstrates favorable outcomes in clinical trials, it could revolutionize the way annular fissures are managed, offering a regenerative treatment option that addresses the underlying cause of disc degeneration. Similarly, if biologic agents prove to be effective in reducing inflammation and promoting disc healing, they could provide a targeted and minimally invasive alternative to traditional treatments.
By participating in clinical trials and contributing to the advancement of medical knowledge, patients, researchers, and healthcare providers play a vital role in shaping the future of annular fissure treatment. It is essential to monitor the progress of ongoing trials and consider their potential implications for improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
In summary, promising advancements in the treatment of annular fissures, such as stem cell therapy and biologic agents, offer new hope for patients suffering from this condition. Ongoing clinical trials are investigating these innovative approaches, and their results may lead to more effective and personalized treatment options in the future.
Lifestyle Modifications and Preventive Measures
Maintaining Spinal Health:
Maintaining spinal health is crucial for preventing and managing conditions like annular fissures. Here are some key strategies:
1. Regular Exercise:
Engaging in regular exercise can strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine, improve flexibility, and support overall spinal health. Activities such as walking, swimming, yoga, and Pilates are particularly beneficial for promoting spinal mobility and reducing the risk of injury.
2. Proper Posture:
Maintaining proper posture is essential for preventing strain on the spine and reducing the risk of developing annular fissures. Whether sitting, standing, or lifting objects, it’s important to keep the spine in a neutral position, with the shoulders back and the ears aligned with the shoulders. Avoiding prolonged periods of sitting and using ergonomic furniture can also help support good posture.
3. Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight is important for reducing the load on the spine and preventing excessive pressure on the intervertebral discs. Excess weight can increase the risk of developing annular fissures and exacerbate existing symptoms. Eating a balanced diet and incorporating regular exercise into your routine can help achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Preventing Recurrence or Exacerbation of Annular Fissures:
Once an annular fissure has been treated, it’s important to take steps to prevent recurrence or exacerbation of symptoms. Here are some strategies:
1. Avoiding Heavy Lifting:
Avoid lifting heavy objects whenever possible, as this can place excessive strain on the spine and increase the risk of re-injury or exacerbation of annular fissures. When lifting, remember to bend at the knees and use proper lifting techniques to reduce stress on the spine.
2. Practicing Safe Body Mechanics:
Practice safe body mechanics during everyday activities to minimize strain on the spine. This includes bending from the knees when picking up objects, avoiding twisting motions, and using proper lifting techniques to protect the back.
3. Maintaining Good Posture:
Consistently practicing good posture can help prevent recurrence of annular fissures. Focus on maintaining a neutral spine alignment while sitting, standing, and moving throughout the day. Using supportive ergonomic furniture and taking regular breaks to stretch can also help alleviate strain on the spine.
4. Staying Active:
Engaging in regular exercise is essential for maintaining spinal health and preventing recurrence of annular fissures. Focus on activities that strengthen the core muscles, improve flexibility, and promote overall fitness. However, be sure to choose low-impact exercises that are gentle on the spine, especially if recovering from an injury.
5. Seeking Prompt Treatment for Symptoms:
If you experience recurrent or worsening symptoms of annular fissures, seek prompt medical attention. Early intervention can help prevent further damage and improve outcomes. Your healthcare provider can recommend appropriate treatment options based on your individual needs and circumstances.
By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can promote spinal health, reduce the risk of recurrence or exacerbation of annular fissures, and enjoy a higher quality of life. Always remember to consult with your healthcare provider before initiating any new exercise regimen or making substantial lifestyle alterations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, managing annular fissures requires a multifaceted approach that considers the individual needs and circumstances of each patient. Here’s a recap of the key points regarding the treatment of annular fissures:
1. Treatment Options:
Treatment options for annular fissures range from conservative measures like rest, physical therapy, and medication to more invasive interventions such as epidural steroid injections, nerve blocks, and surgical procedures like discectomy or spinal fusion.
2. Promising Advancements:
Recent advancements in medical research, including stem cell therapy and biologic agents, offer new hope for the future treatment of annular fissures. These innovative approaches hold the potential to provide targeted, regenerative treatments that address the underlying cause of disc degeneration.
3. Importance of Personalized Care:
Each individual’s experience with annular fissures is unique, and treatment plans should be tailored to their specific needs, preferences, and goals. Seeking personalized medical advice and working closely with healthcare providers is essential for accessing the most appropriate and effective treatment options available.
4. Encouragement to Seek Help:
Individuals dealing with annular fissures are encouraged to seek help and explore comprehensive treatment plans that address their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Don’t hesitate to reach out to healthcare providers for support and guidance in managing your spinal health.
Remember, you are not alone in your journey to manage annular fissures. By seeking personalized medical advice and actively participating in your treatment plan, you can take control of your spinal health and work towards a better quality of life.
References
For more information about Annular fissures you can read also the given website- Read More