Smoking is a habit that has been linked to numerous health issues, and one such often overlooked consequence is smoking causes piles. Scientific studies consistently highlight the undeniable fact: smoking causes piles. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricate relationship between smoking and piles, exploring the mechanisms, health implications, and preventive measures.
The link between smoking and piles, also known as hemorrhoids, is a significant health concern that often goes unnoticed. Piles are swollen and inflamed veins in the rectum and anus, leading to discomfort, pain, and bleeding. Understanding the connection between smoking and piles is crucial for promoting public health awareness.
It’s crucial to understand the health risks involved; one such risk is that smoking causes piles. Research has consistently shown a correlation between smoking and an increased risk of developing piles. The mechanisms behind this link involve the harmful substances present in tobacco, particularly nicotine, which adversely affect blood vessels. Smoking-induced vascular damage can lead to impaired blood circulation in the rectal area, creating an environment conducive to the development and exacerbation of the piles.
Moreover, smoking has profound effects on the digestive system, influencing bowel movements and contributing to constipation, a common precursor to the development of piles. The impact on blood circulation and the digestive tract collectively makes smoking a significant risk factor for piles.
Addressing this link is essential for individuals to make informed lifestyle choices. Individuals can significantly reduce the risk of developing piles by quitting smoking, adopting a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and incorporating regular exercise. Creating awareness about the connection between smoking and piles is crucial for public health education, dispelling myths, and promoting positive lifestyle changes.
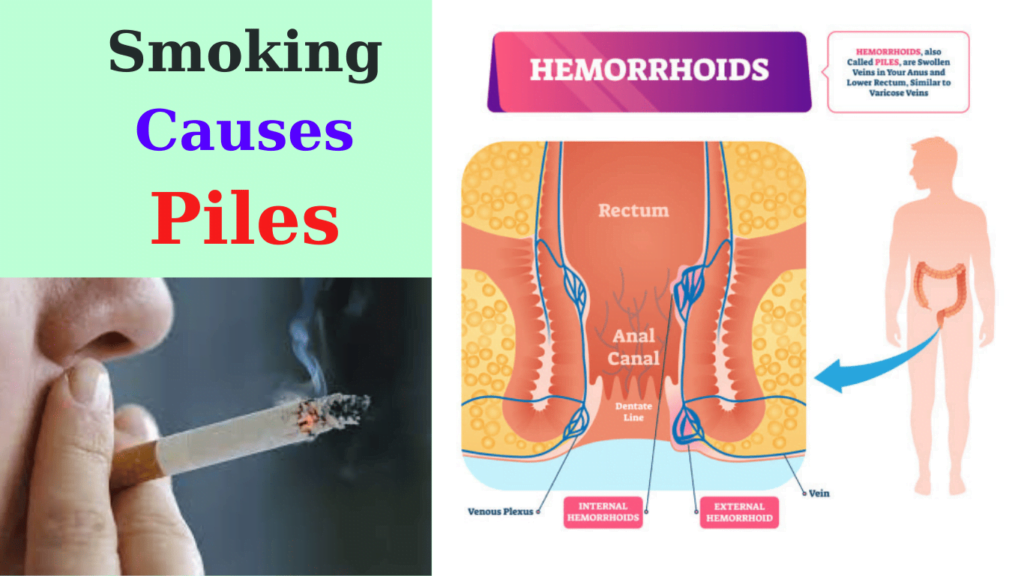
Definition and Explanation of Piles
Table of Contents
- 1 Definition and Explanation of Piles
- 2 Smoking Causes Piles: The Connection/”Is Smoking Good For Piles?”
- 3 Impact on Blood Circulation
- 4 V. Smoking and Digestive System
- 5 Healthy Lifestyle Choices To Reduce Hemorrhoids
- 6 Myths and Misconceptions about Piles: Dispelling Common Fallacies
- 7 Conclusion: Smoking Causes Piles
- 8 FAQ
Hemorrhoids, commonly referred to as piles, are swollen and inflamed veins in the rectum and anus. This condition can lead to discomfort, pain, and bleeding during bowel movements. Piles can be categorized into two main types: internal and external. Internal piles occur inside the rectum and are often painless but may cause bleeding. External piles, on the other hand, develop around the anus and can be more painful.
Common causes of piles include a sedentary lifestyle, poor dietary habits, and prolonged straining during bowel movements. Symptoms may include itching, pain, and blood in the stool. While mild cases can be managed with lifestyle changes, severe cases may require medical intervention, including medications or surgical procedures.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of piles is crucial for early detection and effective management of this common yet often overlooked condition.
Smoking Causes Piles: The Connection/”Is Smoking Good For Piles?”
A. Research Findings on the Connection
Scientific studies have consistently shown a correlation between smoking and an increased risk of developing piles. Exploring these research findings provides insight into the mechanisms at play.
Clarifying its role in the development of piles, smoking, and more specifically, the presence of nicotine plays a detrimental role in contributing to the occurrence and worsening of piles, also known as hemorrhoids.
Nicotine, a major component found in tobacco, has vasoconstrictive properties, meaning it causes blood vessels to narrow. This constriction affects blood circulation, particularly in the rectal area. The impaired blood flow can lead to the development of swollen and inflamed veins, which characterize piles.
In simpler terms, smoking, through the action of nicotine, induces damage to the blood vessels, making them less elastic and more prone to inflammation. This vascular damage, combined with the already delicate nature of the rectal veins, creates an environment conducive to the formation of piles.
Understanding this role is crucial for individuals seeking to mitigate their risk of developing piles. By recognizing the impact of smoking on blood circulation and the subsequent consequences for rectal health, individuals can make informed decisions about their lifestyle choices. Quitting smoking is a key step in breaking this chain of events and promoting better vascular and rectal health.
B. Mechanisms Through Which Smoking Causes Piles
Nicotine and other harmful substances in tobacco have been found to adversely affect the blood vessels in the rectal area, leading to vascular damage and impairing blood circulation in the rectal area, contributing to the development and exacerbation of piles.
C. Increased Risk Factors for Smokers
Smokers face heightened risk factors for piles, including compromised blood circulation and a greater likelihood of developing chronic constipation, a common precursor to piles.
Impact on Blood Circulation
A. Explanation of How Smoking Affects Blood Vessels
The impact of smoking on blood vessels is not confined to the respiratory system. Understanding the broader implications on blood circulation helps explain its role in the development of piles.
B. Connection to Impaired Blood Circulation and Piles
Smoking-induced vascular damage can lead to impaired blood circulation in the rectal area, creating an environment conducive to the development of piles. Smoking causes piles due to restricted blood flow to the particular body parts.
C. Insights into the Role of Nicotine
Nicotine, a major component of tobacco, plays a central role in the constriction of blood vessels, further exacerbating the risk of developing piles for individuals who smoke.
V. Smoking and Digestive System
A. Overview of Smoking’s Impact on the Digestive Tract
Smoking has profound effects on the entire digestive system, influencing everything from the esophagus to the intestines. This section explores how these effects contribute to the development of piles.
The impact of smoking on the digestive tract is profound and extends beyond the well-known respiratory consequences. Smoking affects various components of the digestive system, influencing its functionality and potentially contributing to health issues, including the development of conditions like piles.
1. Nicotine’s Influence:
Nicotine, a primary component of tobacco, directly affects the digestive tract. This substance can lead to increased stomach acid production, disrupting the balance needed for healthy digestion. The consequences of this disruption may include heartburn, acid reflux, and, indirectly, complications like piles.
2. Bowel Movement Alterations:
Smoking has been associated with changes in bowel habits. It can contribute to both constipation and diarrhea, disrupting the regularity of bowel movements. The link between smoking-induced irregular bowel movements and the development of piles is significant, as constipation is a known risk factor for piles.
3. Inflammatory Response:
Smoking triggers an inflammatory response in the body, affecting not only the respiratory system but also the entire digestive tract. Chronic inflammation can contribute to the weakening of blood vessels, making them more susceptible to conditions like piles.
4. Reduced Blood Flow:
Smoking has vasoconstrictive effects, meaning it narrows blood vessels. This reduction in blood flow can compromise the health of the digestive organs, including the rectum. Impaired blood circulation in the rectal area is a contributing factor to the development and exacerbation of piles.
5. Impact on the Microbiome:
The intricate balance of the gut microbiome, crucial for digestion and overall health, can be disrupted by smoking. Changes in the microbial composition may influence digestive processes and contribute to conditions affecting the rectal and anal regions.
6. Association with Gastrointestinal Disorders:
Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of various gastrointestinal disorders, such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. These disorders can further heighten the vulnerability to complications like piles due to the underlying inflammation and disruptions in the digestive system.
Understanding the multifaceted impact of smoking on the digestive tract is essential for individuals aiming to safeguard their overall health. Quitting smoking, coupled with adopting a balanced diet and maintaining regular exercise, is crucial for preventing not only respiratory issues but also digestive complications, including the development of piles.
B. Influence on Bowel Movements and Constipation
Smoking has been linked to alterations in bowel movements and an increased likelihood of constipation. These factors, when combined, can significantly contribute to the development and aggravation of piles.
C. Contribution to the Development of Piles
Understanding the direct and indirect contributions of smoking to the development of piles is essential for individuals looking to mitigate their risk.
Other Health Complications
Beyond its impact on piles, smoking is associated with an unlimited of health complications.
The detrimental effects of smoking extend far beyond the respiratory system, encompassing a myriad of additional health issues that significantly impact overall well-being. Understanding these associated health concerns is crucial for individuals contemplating the decision to quit smoking and embrace a healthier lifestyle. Here, we delve into some of the prominent health issues linked to smoking:
1. Cardiovascular Diseases:
Smoking is a major contributor to cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. The harmful chemicals in tobacco can damage blood vessels, increase blood pressure, and elevate the risk of blood clot formation.
2. Respiratory Disorders:
While commonly known, it’s essential to reiterate that smoking is a primary cause of respiratory disorders such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema. The inhalation of toxic substances damages the lungs, leading to difficulty in breathing and decreased lung function.
3. Cancer Risk:
Smoking is a leading cause of various cancers, including lung, throat, mouth, esophagus, pancreas, bladder, and colorectal cancers. The carcinogens in tobacco smoke lead to the formation of cancerous cells.
4. Weakened Immune System:
The immune system’s ability to ward off infections is compromised by smoking. Smokers are more susceptible to illnesses, and their bodies may take longer to recover from infections compared to non-smokers.
5. Reproductive Issues:
Both male and female reproductive health can be adversely affected by smoking. In men, it can lead to erectile dysfunction, while women may experience fertility issues and complications during pregnancy.
6. Bone Health:
Smoking has been linked to decreased bone density, increasing the risk of fractures and osteoporosis. Weakened bones can pose significant challenges to overall mobility and quality of life.
7. Dental Problems:
Smoking contributes to oral health issues, including gum disease, tooth decay, and teeth staining. The habit can also lead to bad breath and an increased risk of tooth loss.
8. Diabetes Complications:
Smokers with diabetes face an elevated risk of complications, including impaired blood flow, nerve damage, and an increased likelihood of developing cardiovascular issues.
9. Mental Health Impacts:
Smoking has been associated with mental health disorders, including depression and anxiety. Nicotine’s addictive nature can exacerbate these conditions and hinder successful treatment outcomes.
10. Skin Aging:
The chemicals in tobacco smoke accelerate the aging process of the skin, leading to premature wrinkles, fine lines, and a dull complexion.
Quitting Smoking:
Importance and Success Stories of Smoking Cessation
Smoking cessation, or quitting smoking, is a transformative journey with profound implications for both physical and mental well-being. Understanding the importance of quitting and drawing inspiration from success stories can serve as powerful motivation for individuals contemplating or embarking on this challenging yet rewarding path. For individuals seeking motivation to quit smoking, understanding that smoking causes piles is a compelling reason for making positive lifestyle changes.
Importance of Quitting Smoking:
1. Enhanced Respiratory Health:
Quitting smoking is synonymous with improved respiratory function. Over time, the lungs begin to heal, reducing the risk of chronic conditions such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
2. Reduced Cardiovascular Risks:
The risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes, diminishes significantly after quitting smoking. Blood pressure normalizes, and the heart undergoes positive changes.
3. Cancer Prevention:
Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to lower the risk of various cancers associated with tobacco use. The body’s natural defense mechanisms against cancer are bolstered with smoking cessation.
4. Enhanced Immune Function:
The immune system rebounds after quitting smoking, better equipped to fend off infections and illnesses. This resilience contributes to an overall improvement in health.
5. Improved Mental Health:
Smoking cessation has positive effects on mental health, reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression. The mental clarity gained can enhance the quality of life.
6. Enhanced Fertility:
For individuals facing fertility challenges, quitting smoking can improve reproductive health. Both male and female fertility can benefit from a smoke-free lifestyle.
7. Economic Benefits:
Quitting smoking leads to substantial financial savings. The costs associated with purchasing cigarettes and potential medical expenses due to smoking-related illnesses are significantly reduced.
Success Stories of Smoking Cessation:
Jane’s Journey to Health:
Jane, a former smoker of 15 years, decided to quit for the sake of her family and personal well-being. Embracing a combination of counseling and nicotine replacement therapy, she successfully quit smoking. Today, Jane enjoys improved lung capacity, and increased energy, and is an advocate for smoking cessation.
John’s Triumph Over Addiction:
John’s journey to quit smoking involved perseverance and support. With the assistance of a support group and behavioral therapy, John overcame the challenges of nicotine addiction. His success story inspires others to seek help and stay committed to a smoke-free life.
Lisa’s Positive Lifestyle Transformation:
Lisa, a long-term smoker, decided to quit to lead a healthier life. Engaging in regular exercise and adopting a balanced diet were integral to her smoking cessation journey. Lisa’s story highlights the holistic benefits of quitting, from improved physical health to a positive mindset.
Conclusion:
Quitting smoking is a pivotal decision that not only impacts individual health but also contributes to a healthier community. The importance of smoking cessation is underscored by the numerous success stories of individuals who have reclaimed their health and well-being. Every successful quit story reinforces the notion that overcoming this challenge is not only possible but immensely rewarding. Whether for personal health, family, or financial reasons, quitting smoking is a courageous and life-affirming choice.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices To Reduce Hemorrhoids
Practical Tips on Incorporating Dietary Changes for Improved Digestive Health
Maintaining a healthy diet is crucial for promoting digestive health and preventing conditions like piles. Here are practical tips on incorporating dietary changes for optimal digestive well-being:
1. Increase Fiber Intake:
– Tip: Gradually introduce fiber-rich foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables into your meals.
– Why: Fiber adds bulk to stools, preventing constipation—a common risk factor for piles.
2. Stay Hydrated:
– Tip: Aim for at least 8 glasses of water daily and include hydrating foods like watermelon and cucumber.
– Why: Hydration supports smooth digestion and helps prevent constipation.
3. Balance Your Plate:
– Tip: Create balanced meals with a mix of lean proteins, whole grains, and colorful vegetables.
– Why: A well-balanced diet provides essential nutrients for overall health, including digestive function.
4. Limit Processed Foods:
– Tip: Gradually reduce intake of processed and high-fat foods.
– Why: Processed foods can be low in fiber and contribute to digestive issues; opting for whole foods is beneficial.
5. Include Probiotics:
– Tip: Add yogurt, kefir, or fermented foods to your diet.
– Why: Probiotics promote a healthy gut microbiome, aiding in digestion and immune function.
6. Moderate Spicy Foods:
– Tip: Control spice levels in your meals, especially if sensitive to spicy foods.
– Why: Spicy foods may irritate the digestive tract; moderation can help prevent discomfort.
7. Mindful Eating:
– Tip: Eat slowly, savoring each bite, and pay attention to hunger and fullness cues.
– Why: Mindful eating aids digestion and helps prevent overeating.
8. Herbal Teas for Comfort:
– Tip: Choose soothing herbal teas like peppermint or chamomile.
– Why: Herbal teas can ease digestive discomfort and promote relaxation.
9. Limit Caffeine and Alcohol:
– Tip: Moderate coffee and alcohol consumption.
– Why: Excessive caffeine and alcohol can contribute to dehydration and digestive issues.
10. Small, Frequent Meals:
– Tip: Opt for smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day.
– Why: This approach can aid digestion and prevent bloating.
11. Mind Your Portions:
– Tip: Be mindful of portion sizes to prevent overeating.
– Why: Controlling portions supports healthy digestion and weight management.
12. Include High Antioxidant Foods:
– Tip: Embrace colorful fruits and vegetables rich in antioxidants.
– Why: Antioxidants combat inflammation and promote overall digestive health.
Incorporating these practical tips into your daily routine can contribute to improved digestive health and a reduced risk of conditions like piles. Remember to make changes gradually and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice based on your specific health needs.
Regular Exercise and Its Vital Role in Preventing Piles
Regular exercise is not only crucial for overall health and well-being but also plays a significant role in preventing the development of piles, also known as hemorrhoids. Understanding the connection between physical activity and a healthy digestive system sheds light on the importance of incorporating exercise into our daily routines.
1. Enhanced Blood Circulation:
– How it Helps: Exercise promotes improved blood circulation throughout the body, including the rectal area.
– Why it Matters: Enhanced blood flow helps prevent the formation of swollen and inflamed veins, a primary factor in the development of piles.
2. Prevention of Constipation:
– How it Helps: Regular exercise aids in maintaining regular bowel movements.
– Why it Matters: Constipation is a known risk factor for piles; exercising regularly helps prevent constipation and promotes smoother bowel movements.
3. Weight Management:
– How it Helps: Exercise contributes to weight maintenance or loss, reducing the risk of obesity-related conditions.
– Why it Matters: Being overweight or obese can strain the rectal veins, increasing the likelihood of developing piles.
4. Muscle Tone Improvement:
– How it Helps: Targeted exercises, especially those involving the pelvic floor, contribute to improved muscle tone.
– Why it Matters: Stronger muscles in the pelvic area provide better support for rectal veins, reducing the risk of hemorrhoids.
5. Stress Reduction:
– How it Helps: Exercise is a natural stress reliever, promoting mental well-being.
– Why it Matters: Stress and mental strain can contribute to digestive issues; a relaxed mind supports a healthy digestive system.
6. Prevention of Sedentary Lifestyle Complications:
– How it Helps: Regular physical activity counteracts the effects of a sedentary lifestyle.
– Why it Matters: Prolonged sitting or inactivity can lead to poor circulation and contribute to the development of piles.
7. Improved Digestive Function:
– How it Helps: Exercise stimulates the digestive system and aids in the efficient processing of food.
– Why it Matters: An efficiently functioning digestive system reduces the likelihood of constipation and other digestive issues associated with piles.
8. Holistic Health Benefits:
– How it Helps: Exercise contributes to overall health, reducing the risk of various health conditions.
– Why it Matters: A healthy body is better equipped to prevent and manage conditions such as piles.
Incorporating a variety of exercises into your routine, including cardiovascular exercises, strength training, and targeted pelvic floor exercises, can significantly contribute to preventing piles. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week and consult with a healthcare professional before starting a new exercise regimen, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions. Regular physical activity not only supports a healthy digestive system but also enhances overall quality of life.
Myths and Misconceptions about Piles: Dispelling Common Fallacies
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are a common but frequently misunderstood condition. Unfortunately, numerous myths and misconceptions surround piles, leading to confusion and misinformation. Let’s debunk some of the prevalent fallacies to promote a better understanding of this condition:
Myth 1: Piles Only Affect the Elderly
Fact: Piles can occur at any age, not just in the elderly. Factors such as a sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, and genetic predisposition can contribute to the development of piles in individuals of all ages.
Myth 2: Piles are Always Painful
Fact: While external piles can be painful, internal piles may not cause pain. Symptoms vary, and some individuals may experience itching, bleeding, or discomfort rather than intense pain.
Myth 3: Piles are Contagious
Fact: Piles are not contagious. They develop due to a combination of factors such as straining during bowel movements, chronic constipation, or prolonged sitting. You cannot “catch” piles from someone else.
Myth 4: Only Unhealthy Individuals Get Piles
Fact: Piles can affect individuals of all health statuses. While poor lifestyle choices may contribute, factors like genetics and pregnancy can also play a role. Healthy individuals can develop piles too.
Myth 5: Piles Result from Spicy Foods Alone
Fact: Spicy foods do not directly cause piles. However, an excessively spicy diet may exacerbate symptoms in individuals who already have piles. The primary contributors to piles are factors like constipation and straining during bowel movements.
Myth 6: Piles Always Require Surgery
Fact: Surgery is usually a last resort for severe cases. Most piles can be managed with lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, and non-surgical treatments. Only a small percentage of individuals with piles require surgical intervention.
Myth 7: Sitting on Cold Surfaces Causes Piles
Fact: Piles are not caused by sitting on cold surfaces. The development of piles is more closely associated with factors like straining during bowel movements, chronic constipation, and lack of physical activity.
Myth 8: Piles Will Go Away on Their Own
Fact: While some mild cases may improve with lifestyle changes, ignoring persistent symptoms can lead to complications. Seeking medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment is crucial to managing piles effectively.
Myth 9: Piles and Colorectal Cancer are the Same
Fact: Piles and colorectal cancer are distinct conditions. Piles involve swollen veins in the rectum and anus, while colorectal cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the colon or rectum. However, persistent bleeding from the rectum should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Myth 10: Piles Are a Result of Poor Personal Hygiene
Fact: Personal hygiene is important, but it is not the sole factor in developing piles. Piles are more closely linked to issues like constipation, straining during bowel movements, and lifestyle factors.
Dispelling these myths is essential for promoting accurate information about piles. If you suspect you have piles or experience persistent symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and guidance on effective management.
Conclusion: Smoking Causes Piles
In conclusion, understanding the realities of piles and dispelling prevalent myths is crucial for promoting accurate information and fostering a proactive approach to digestive health. Smoking causes piles, or hemorrhoids, are a common but induced condition that can affect individuals of all ages, and awareness plays a pivotal role in prevention and management.
From recognizing the link between smoking and piles to embracing lifestyle changes such as regular exercise and a fiber-rich diet, individuals can take proactive steps to mitigate the risk of piles. It is essential to acknowledge that piles are not exclusive to the elderly, and a holistic understanding of contributing factors is vital for tailored prevention strategies.
Moreover, debunking misconceptions about piles, such as the notion that they are contagious or always require surgery, helps individuals make informed decisions about their health. Piles, while potentially uncomfortable, can often be managed with non-surgical interventions and lifestyle adjustments. When discussing the potential consequences of smoking, it’s essential to acknowledge that smoking causes piles.
By incorporating practical tips, embracing a balanced diet, and maintaining an active lifestyle, individuals can contribute to their overall digestive well-being and reduce the likelihood of developing piles. Seeking medical advice for persistent symptoms is crucial, as early detection and intervention can prevent complications and ensure effective management.
In essence, knowledge is the key to empowerment when it comes to preventing and managing piles. The journey to digestive health involves a combination of lifestyle choices, awareness, and a proactive mindset. By dispelling myths and embracing accurate information, individuals can navigate the path to optimal digestive well-being and enjoy a higher quality of life.
FAQ
1. Is smoking good for piles?
No, smoking is not good for piles. It can increase the risk of the piles.
2. Can I smoke in piles?
No, You should avoid it because smoking causes piles, it is proven in research.
3. Is smoking bad for piles?
Yes, Smoking causes piles is confirmed by the scientists.




